Interval List Intersections
PROBLEM
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a<=b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a<=x<=b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1
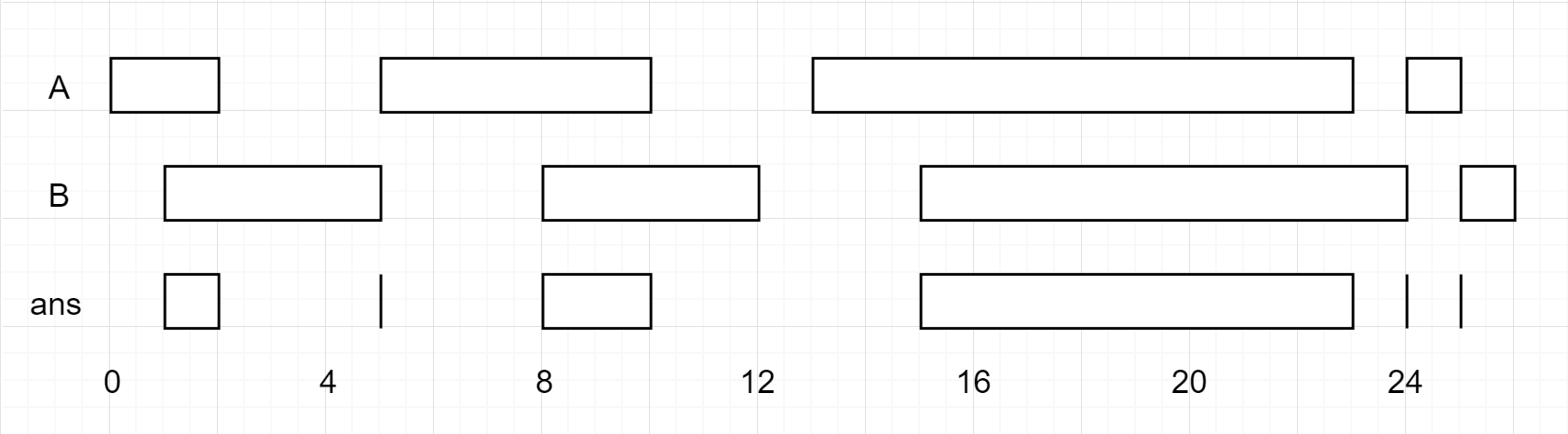
*Input*: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
*Output*: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2
*Input*: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = []
*Output*: []
SOLVING
We’ll use Two Pointers method to solve this problem.
Steps
- Create the variable
result - Place
LeftPtrto first list infirstListandRightPtrto first list insecondList - While
LeftPtrandRightPtraren’t superior offirstListandrightListsize:Startvalue of theintersectedListequalmaxbetween first element ofLeftPtrandRightPtrEndvalue of theintersectedListequalminbetween last element ofLeftPtrandRightPtr- If
Startis inferior or equal toEndyou can push yourintersectedListtoresult - if
Endequal toLeftPtrlast element, increaseLeftPtrotherwiseRightPtr
- Return
result
Code
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>> &firstList,
vector<vector<int>> &secondList) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int leftPtr = 0;
int rightPtr = 0;
while (leftPtr < firstList.size() && rightPtr < secondList.size()) {
vector<int> intersectedList;
int start = max(firstList[leftPtr][0], secondList[rightPtr][0]);
int end = min(firstList[leftPtr][1], secondList[rightPtr][1]);
if (start <= end) result.push_back({start, end});
(end == firstList[leftPtr][1]) ? leftPtr++ : rightPtr++;
}
return result;
}
};